Cities in the Alliance

Having faced environmental, economic and social crises, industrial legacy cities are champions in reinventing themselves and turning challenges into opportunities. The Urban Transitions Alliance will be guided by their joint vision of well-managed transitions towards a sustainable future, which centers on a healthy environment and just opportunities for their citizens.
These cities are working together to achieve sustainable urban transitions
Baltimore, MD, USA
Over the 20th century, Baltimore grew into one of America’s largest cities and one of its most commercially important centers, also leading in manufacturing chrome, copper, and steel products.
The efforts around greening and building a more sustainable city have led to the creation of the Baltimore Office of Sustainability in 2007.
Learn more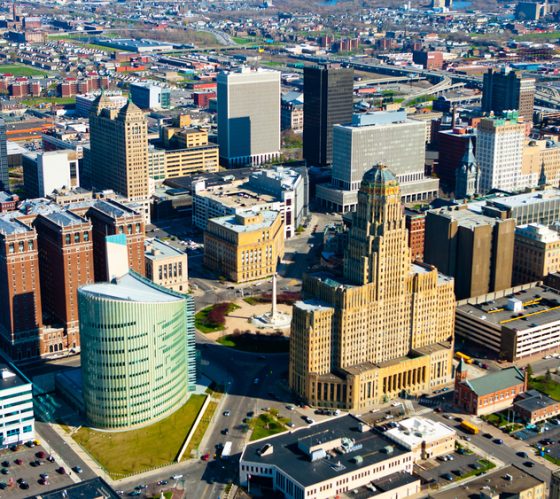
Buffalo, NY, USA
Buffalo, New York served as gateway between the Northeast and Midwest markets, quickly transforming into a steel and automotive industrial boom town.
Buffalo redevelopment actions focus on cleaning up legacy pollution while developing more sustainable and resilient urban systems.
Learn more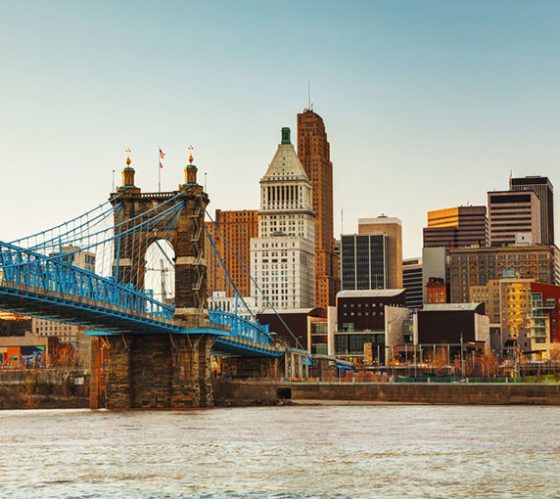
Cincinnati, OH, USA
Cincinnati rapidly developed initially as a meatpacking center before diversifying into a soap and lotions hub, ultimately becoming a leading industrial city. The environmental impact of unsustainable production and waste management has had a lasting impact.
Cincinnati plans to be a leading city in the global energy transition. The city aims to be powered by 100 percent renewable energy by 2035, which includes development of the largest municipal solar array in the United States at 25 megawatts.
Learn more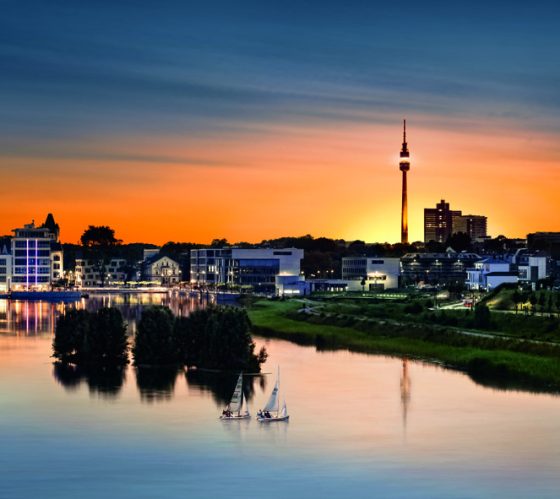
Dortmund, Germany
As the largest city in the Ruhr metropolitan region, Dortmund and the surrounding Emscher region was the engine of the industrial revolution in Germany.
Dortmund recognized the signs of structural change and embarked on its urban transition early on. The first wave of the transition initiatives led to significant gains in tertiary sectors, including insurance and financial services, research and development and new technologies.
Learn more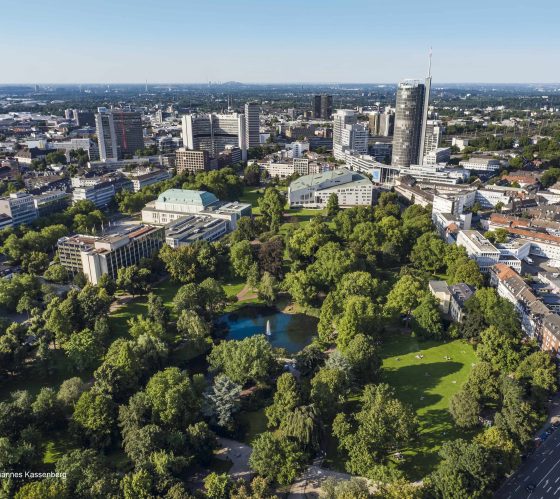
Essen, Germany
Since the early 19th century, coal mining and steel production fueled rapid economic growth in Essen, turning the Ruhr Region into the industrial heart of Germany. This rapid industrialization process has impacted environmental quality and natural resources.
Essen’s economy has developed into a service and financial center for the region, and the city has focused on spatial redevelopment and nature restoration as part of its urban transition.
Learn more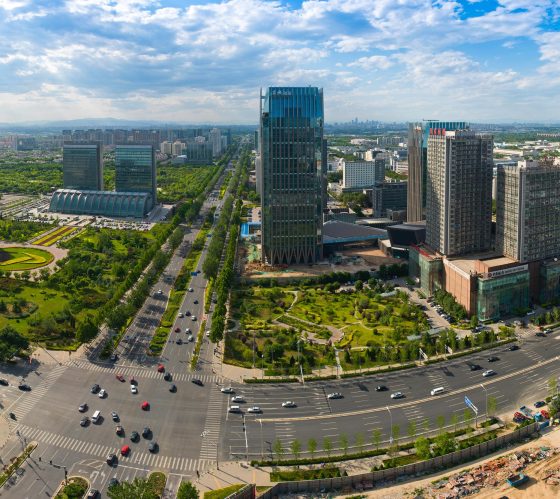
Economic-Technological Development Area (BDA), Beijing, China
Information and communication technology, bioengineering, automobile, and equipment manufacturing industries are active in BDA.
BDA aims to move away from energy-intensive, low-value manufacturing and introduce integrated water and waste management systems.
Learn more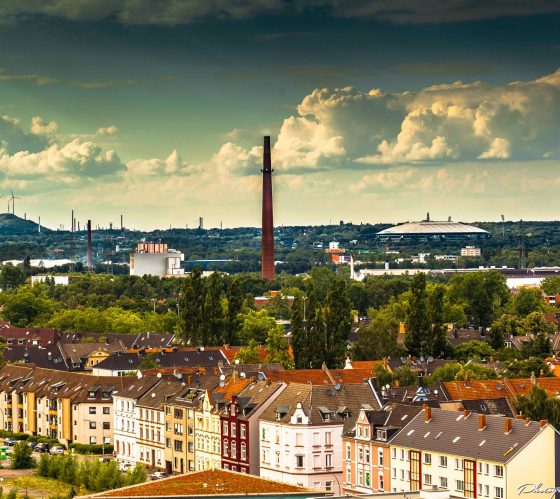
Gelsenkirchen, Germany
Gelsenkirchen is part of the Ruhr region, where coal mining, steel production and electricity generation is concentrated in Germany. During the industrial era, Gelsenkirchen was one of Europe’s major coal and steel cities.
The city places strong emphasis on education to support its transition, seeing education as the key to sustainable development.
Learn more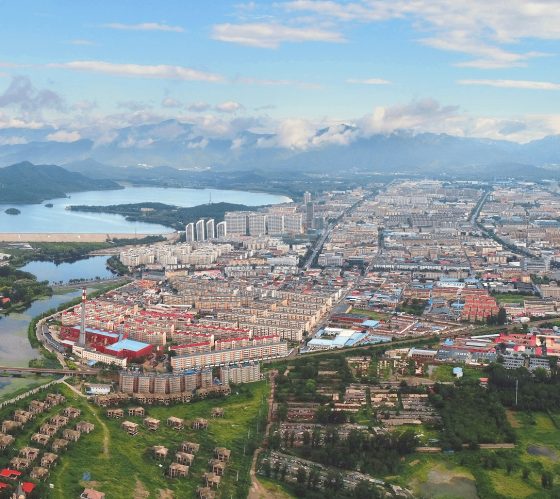
Huairou District, Beijing, China
While experiencing constant economic and industrial growth, Huairou District is undergoing a transition within its industrial structure. Recent decades have seen mining and cement industries with high pollution emissions and high energy consumption shrink or forced to close.
Recognizing that its future relies on sustainable development and conserving its surrounding natural resources, Beijing Huairou District has emerged from a legacy of agricultural and industrial production to a thriving satellite district that prioritizes new industries and natural resource conservation.
Learn more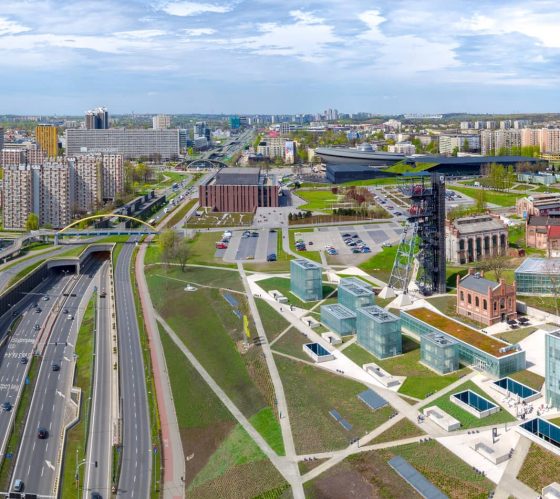
Katowice, Poland
Katowice became an industrial powerhouse by the end of the 18th century with the discovery of rich coal resources. Strong industrial development quickly became a fundamental aspect of the identity of citizens, the natural environment and the economic foundation of the city.
Katowice is now looking to overcome environmental challenges arising from its industrial era with both short and long term solutions
Learn more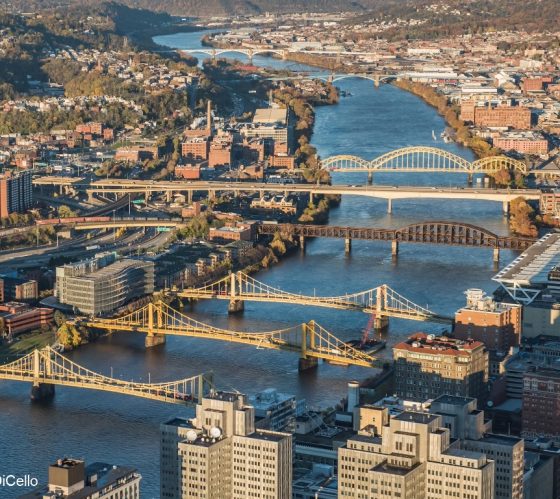
Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Pittsburgh, known for its legacy as a steel city, experienced decades of deindustrialization, suburbanization and an urban-regional economic slowdown in the early 1980s.
To address the significant environmental and economic consequences of its industrial legacy, Pittsburgh has advanced a number of ambitious environmental and climate actions intertwined with its plans for economic growth.
Learn more
Yuhua District, Shijiazhuang, China
As a heavily industrialized area, Shijiazhuang is facing serious environmental consequences from rampant industrial expansion. It continually ranks among the cities most impacted by air pollution in China and faces risks of worsening smog and weather storms.
The city has invested in a multi-year urban redevelopment plan which will expansion transport corridors, lead to land use restructuring, housing construction, and the establishment of green areas.
Learn more
